Published On:Friday, 9 December 2011
Posted by Muhammad Atif Saeed
Linear Inequalities
Linear Inequalities
An inequality is a sentence using a symbol other than the equals sign (=). The most common inequality symbols are <, ≤, >, and ≥. To solve an inequality sentence, use exactly the same procedure that you would if it were an equation, with the following exception. When multiplying (or dividing) both sides of an inequality by a negative number, the direction of the inequality switches. This is called the negative multiplication property of inequality.If a, b, and c are real numbers and c is negative, and a < b, then ac > bc. Or if a > b, then ac < bc.
Example 1
Solve for x: 3 x – 7 > 20.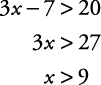
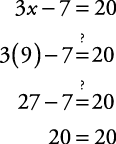
{ x| x > 9}
This is read as “the set of all x so that x is greater than 9.” Many times, the solutions to inequalities are graphed to illustrate the answers. The graph of { x| x > 9}is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. Note that 9 is not included.
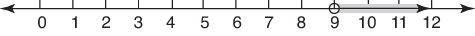
Example 2
Solve for x: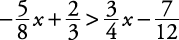 .
. The LCD for the denominators in this inequality is 24. Multiply both sides of the inequality by 24 as you would have had this been an equation.
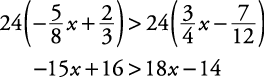
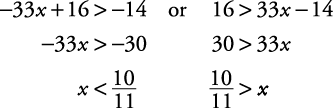
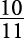 . The check is left to you. The solution set is expressed as
. The check is left to you. The solution set is expressed as 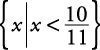
Figure 2. Note the hole at 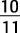 .
.
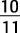 .
. 









