Published On:Friday, 9 December 2011
Posted by Muhammad Atif Saeed
Absolute Value Equations
Absolute Value Equations
Recall that the absolute value of a number represents the distance that number is from zero on the number line. The equation | x| = 3 is translated as “ x is 3 units from zero on the number line.” Notice, on the number line shown in Figure 1, that two different numbers are 3 units away from zero, namely, 3 and –3.Figure 1. Absolute value.
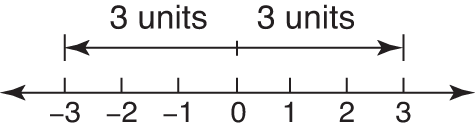
Example 1
Solve for x: |4 x – 2| = 8.This translates to “4 x – 2 is 8 units from zero on the number line” (see Figure 2).
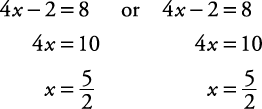
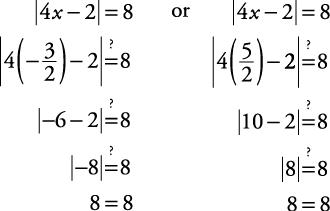
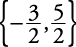 .
. Figure 2. There are + and – solutions.
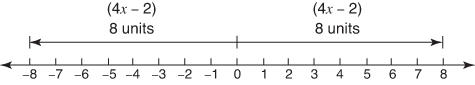
Example 2
Solve for x: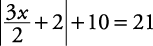
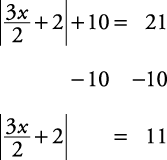
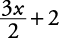 is 11 units from zero on the number line.”
is 11 units from zero on the number line.” 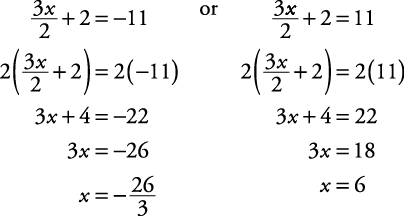
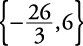 .
. Example 3
Solve for x: | x | = –2.This problem has no solutions, because the translation is nonsensical. Distance is not measured in negative values.
Example 4
Solve for x: |2 x – 3| = |3 x + 7|.This type of sentence will be true if either
- The expressions inside the absolute value symbols are exactly the same (that is, they are equal); or
- The expressions inside the absolute value symbols are opposites of each other.

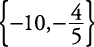 .
. Example 5
Solve for x: | x – 2| = |7 – x|.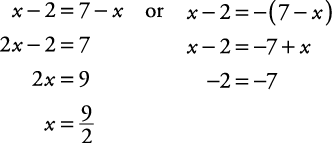
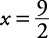 .
. Check the solution.
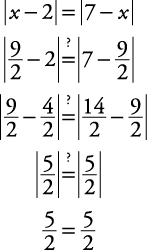
 .
. 








