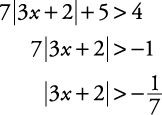Published On:Friday, 9 December 2011
Posted by Muhammad Atif Saeed
Absolute Value Inequalities
Absolute Value Inequalities
Remember, absolute value means distance from zero on a number line. | x| < 4 means that x is a number that is less than 4 units from zero on a number line (see Figure 1).Figure 1. Less than 4 from zero.
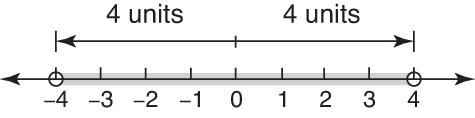

Figure 2. More than 4 from 0.
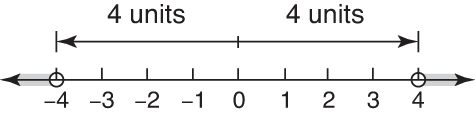
{ x| x < –4 or x > 4}
| x| < 0 has no solutions, whereas | x| > 0 has as its solution all real numbers except 0. | x| > –1 has as its solution all real numbers, because after taking the absolute value of any number, that answer is either zero or positive and will always be greater than –1. The following is a general approach for solving absolute value inequalities of the form
- | ax + b| < c or | ax + b| > c
- | ax + b| ≤ c or | ax + b| ≥ c
- If c is negative,
- | ax + b| < c has no solutions.
- | ax + b| ≤ c has no solutions.
- | ax + b| > c has as its solution all real numbers.
- | ax + b| ≥ c has as its solution all real numbers.
- If c = 0,
- | ax + b| < 0 has no solutions.
- | ax + b| ≤ 0 has as its solution the solution to ax + b = 0.
- | ax + b| > 0 has as its solution all real numbers, except the solution to ax + b = 0.
- | ax + b| ≥ 0 has as its solution all real numbers.
- If c is positive,
- | ax + b| < c has solutions that solve
ax + b > – c and ax + b < c – c < ax + b < cThat is:
- | ax + b| > c has solutions that solve
ax + b < – c or ax + b > c - | ax + b| ≤ c has solutions that solve
– c ≤ ax + b ≤ c - | ax + b| ≥ c has solutions that solve
ax + b ≤ – c or ax + b ≥ c
- | ax + b| > c has solutions that solve
- | ax + b| < c has solutions that solve
Example 1
Solve for x: |3 x – 5| < 12.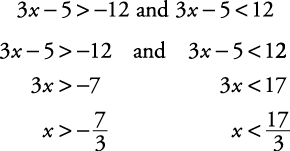
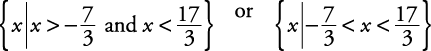
Figure 3. x is greater than 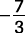 and less than
and less than 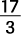 .
.
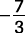 and less than
and less than 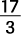 .
. 
Example 2
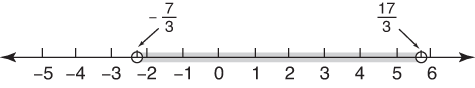
Solve this disjunction for x: |5 x + 3| > 2.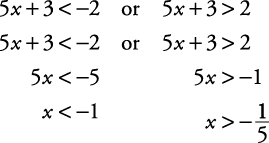
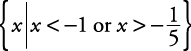 . The graph of the solution set is shown in Figure 4.
. The graph of the solution set is shown in Figure 4. Figure 4. x is less than –1 or greater than 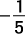 .
.
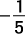 .
. 
Example 3
Solve for x: |2 x + 11| < 0.There is no solution for this inequality.
Example 4
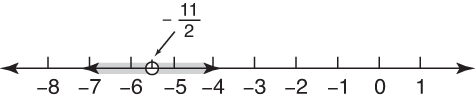
Solve for x: |2 x + 11| > 0.The solution is all real numbers except for the solution to 2 x + 11 = 0. Therefore,
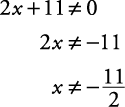
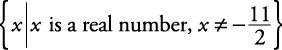 . The graph of the solution set is shown in Figure 5.
. The graph of the solution set is shown in Figure 5. Figure 5. All numbers except 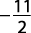 .
.
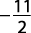 .
. 
Example 5
Solve for x: 7|3 x + 2| + 5 > 4.First, isolate the e xpression involving the absolute value symbol.